Proper counterbalance valve selection ensures critical system safety. It prevents load runaway and maintains control. The right counterbalance valve enhances operational stability, providing smooth movement. This choice directly links to overall hydraulic system efficiency. Hanshang offers reliable components.
Key Takeaways
- Counterbalance valves are important for safety. They stop heavy loads from falling fast. They also keep loads steady.
- Choosing the right valve is key. Match its power to your load. Also, pick the right pilot ratio for steady or smooth movement.
- Check and care for your valves often. Look for leaks or strange sounds. This helps your hydraulic system work well and last longer.
Understanding the Counterbalance Valve
What is a Counterbalance Valve?
A counterbalance valve is a crucial component in hydraulic systems. It acts as a safety device. This valve maintains control over a hydraulic actuator, especially when it supports a load. It prevents uncontrolled movement. The valve ensures the load remains stable.
Core Functions of a Counterbalance Valve
This valve performs several vital functions. It holds a load in position. This prevents the load from drifting or falling. The valve also controls the speed of a descending load. It creates back pressure, which regulates the flow out of the actuator. Furthermore, it prevents cavitation in the hydraulic cylinder. Cavitation can damage the system. The counterbalance valve ensures smooth and controlled motion.
How Counterbalance Valves Prevent Load Runaway
Load runaway occurs when a heavy load moves uncontrollably due to gravity. A counterbalance valve prevents this dangerous situation. It requires a pilot pressure to open. This pilot pressure comes from the inlet side of the actuator. When the operator commands movement, pressure builds. This pressure then opens the valve. The valve only allows fluid to exit the cylinder at a controlled rate. If the operator releases the control, the valve closes. This action locks the load in place. It ensures the load does not accelerate beyond a safe speed.
Key Criteria for Counterbalance Valve Selection
Selecting the correct counterbalance valve is crucial for system performance and safety. Engineers must consider several factors. These factors ensure the valve operates effectively within its intended application.
Matching Load Capacity and Pressure Ratings
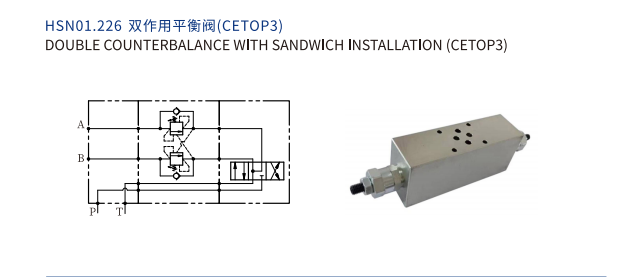
System designers must first match the counterbalance valve’s load capacity to the maximum load it will support. This ensures the valve can safely hold the load without failure. They also need to consider the pressure ratings. The valve’s maximum operating pressure must exceed the highest pressure the hydraulic system will generate. This prevents damage to the valve and maintains system integrity. For example, Hanshang’s HSN01.226 double-acting counterbalance valve handles up to 350 bar. This rating makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications. The valve’s set pressure should be at least 1.3 times the maximum load pressure. This provides a safety margin.
Selecting the Optimal Pilot Ratio for Counterbalance Valves
The pilot ratio significantly impacts a counterbalance valve’s control characteristics. This ratio determines how much pilot pressure is needed to open the valve. A lower pilot ratio offers greater stability. It requires more pilot pressure to open, making the valve less sensitive to pressure fluctuations. This is ideal for applications needing precise load control. A higher pilot ratio provides smoother operation. It requires less pilot pressure to open, allowing for quicker response times. This suits applications where rapid movement is necessary. Engineers must align the pilot ratio with the specific application needs. This ensures both stability and responsiveness.
Considering Flow Rate for Counterbalance Valve Performance
The flow rate through the counterbalance valve directly affects its performance. Engineers must select a valve with a flow capacity that matches the system’s maximum flow requirements. An undersized valve restricts flow. This can cause excessive heat generation and pressure drops. An oversized valve might lead to sluggish response or instability. Proper sizing ensures efficient fluid movement. It also prevents cavitation and maintains smooth operation. The valve’s internal passages must accommodate the expected flow without creating undue resistance.
Environmental and Application Factors for Counterbalance Valves
Environmental conditions and specific application requirements also influence valve selection. Extreme temperatures, corrosive environments, or high vibration levels demand specialized valve materials and designs. For instance, marine applications require corrosion-resistant components. Mobile machinery might need valves designed to withstand shock and vibration. The type of hydraulic fluid used also plays a role. Compatibility between the fluid and valve seals is essential. Engineers must also consider the physical space available for installation. Compact designs, like Hanshang’s cartridge-style HSN01.226, offer flexibility in tight spaces. These factors ensure the chosen counterbalance valve performs reliably throughout its service life.
The Impact of Pilot Ratios on Counterbalance Valve Control
The pilot ratio is a critical design parameter for any counterbalance valve. It directly influences how the valve responds to system pressures. This ratio determines the amount of pilot pressure required to open the valve. Understanding its impact helps engineers optimize system performance.
Low Pilot Ratios for Enhanced Stability
A low pilot ratio provides superior stability for hydraulic systems. This design requires a significant increase in pilot pressure to open the valve. Consequently, the valve becomes less sensitive to minor pressure fluctuations. This characteristic prevents unintended movement or “chatter” in the actuator. Systems handling heavy, suspended loads greatly benefit from low pilot ratios. For example, a crane lifting a large object needs maximum stability. The low ratio ensures the load remains securely held. It only moves when the operator intentionally applies sufficient pressure. This design prioritizes safety and precise load positioning.
High Pilot Ratios for Smoother Operation
Conversely, a high pilot ratio promotes smoother and more responsive operation. This design requires less pilot pressure to open the valve. The valve reacts more quickly to changes in system pressure. This allows for a more fluid and continuous motion of the actuator. Applications demanding rapid and smooth cycling often utilize high pilot ratios. Consider a machine performing repetitive, light-duty tasks. A high pilot ratio minimizes jerky movements. It provides a more comfortable and efficient user experience. This design optimizes for speed and operational fluidity.
Aligning Pilot Ratio with Application Needs
Selecting the correct pilot ratio is a crucial engineering decision. It involves balancing the need for stability against the desire for smooth operation. Engineers must carefully assess the application’s specific requirements.
- Heavy, Critical Loads: Applications involving heavy, potentially dangerous loads demand a low pilot ratio. This ensures maximum control and prevents accidental load runaway.
- Light, Repetitive Tasks: Systems performing lighter, frequent movements benefit from a high pilot ratio. This provides quicker response times and smoother transitions.
- Dynamic Conditions: Some applications experience varying load conditions. Engineers might choose a moderate pilot ratio. This offers a compromise between stability and responsiveness.
The optimal pilot ratio directly impacts system efficiency and safety. A well-chosen ratio ensures the counterbalance valve performs its function reliably. It also contributes to the overall longevity of the hydraulic system.
Troubleshooting Common Counterbalance Valve Issues
Hydraulic systems rely on proper valve function. Operators often encounter specific problems with these components. Identifying and resolving these issues quickly maintains system efficiency and safety.
Addressing Counterbalance Valve Chatter and Instability
Chatter or instability indicates an issue with valve operation. This often results from an incorrect pilot ratio setting. Sometimes, air in the hydraulic system causes erratic movement. Contaminated fluid can also impede smooth valve action. Technicians should verify the pilot ratio matches application requirements. They must bleed air from the system. Regular fluid filtration prevents contamination. Adjusting the damping orifice can also stabilize valve response.
Resolving Load Drift and Creep in Counterbalance Valves
Load drift or creep means the actuator slowly moves without command. Internal leakage within the valve often causes this problem. Worn seals or damaged valve seats allow fluid to bypass. An incorrect pressure setting can also contribute to drift. Maintenance personnel should inspect valve seals for wear. They must replace any damaged components. Recalibrating the valve’s pressure setting ensures proper load holding.
Managing Overheating and Pressure Spikes
Excessive heat and sudden pressure spikes harm hydraulic systems. An undersized valve can restrict flow, generating heat. Rapid cycling of the actuator also contributes to overheating. Pressure spikes often occur due to sudden load changes or improper valve adjustments. Engineers should ensure the valve is correctly sized for the system’s flow rate. They can install a larger heat exchanger to manage temperature. Adjusting relief valve settings helps mitigate pressure spikes.
Diagnosing External Leakage and Contamination
External leakage is visible fluid loss around the valve. This typically points to damaged O-rings or loose fittings. Contamination, though not always visible externally, manifests as sluggish operation or premature wear. Technicians must tighten all connections. They should replace worn or cracked seals immediately. Regular fluid analysis and filter changes prevent contamination from damaging internal components.
Advancements in Counterbalance Valve Technology
Hydraulic system technology continually evolves. Manufacturers introduce new features. These innovations enhance performance, efficiency, and reliability.
Integrated Smart Counterbalance Valve Solutions
Modern designs incorporate smart features. These solutions often include embedded sensors. Sensors monitor pressure, temperature, and flow in real-time. They transmit data to control systems. This allows for predictive maintenance. Operators can identify potential issues before failure occurs. This integration improves system uptime.
Energy-Efficient Counterbalance Valve Designs
New designs prioritize energy conservation. Engineers optimize internal flow paths. This reduces pressure drops across the valve. Lower pressure drops mean less energy loss. These designs also minimize heat generation. This contributes to overall system efficiency. It also extends the lifespan of hydraulic fluids and components.
Innovations in Counterbalance Valve Materials and Durability
Material science drives significant improvements. Manufacturers use advanced alloys and specialized coatings. These materials resist wear and corrosion better. They withstand harsh operating environments. This enhances the durability of the counterbalance valve. It also extends its service life. This reduces maintenance frequency and costs.
Digital Control Integration for Counterbalance Valves
Digital control systems offer precise management. Electronic signals control valve operation. This allows for fine-tuning of performance parameters. Operators can adjust settings remotely. Digital integration enables adaptive control. The system can respond dynamically to changing load conditions. This provides superior control and flexibility.
Best Practices for Counterbalance Valve Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and consistent maintenance ensure optimal performance and longevity for hydraulic components. These practices prevent costly downtime and enhance system safety.
Proper Installation Techniques for Counterbalance Valves
Installers must mount valves securely. They should follow manufacturer specifications for torque settings. Ensure correct port connections. Incorrect plumbing can lead to system malfunction. Use appropriate thread sealants. Avoid overtightening fittings. This prevents damage to valve bodies or ports. Clean all hydraulic lines before installation. Contaminants can cause immediate operational issues.
Regular Inspection and Testing of Counterbalance Valves
Operators should conduct visual inspections regularly. Look for signs of external leakage. Check for corrosion or physical damage. Listen for unusual noises during operation. Technicians must periodically test valve functionality. They verify correct pressure settings. They also confirm smooth operation under load. Document all inspection and testing results. This creates a valuable maintenance history.
Establishing Preventative Maintenance Schedules
Implement a strict preventative maintenance schedule. This includes routine fluid analysis. Change hydraulic filters at recommended intervals. Replace seals and O-rings before they fail. Hanshang recommends specific service periods for its products. Adhering to these schedules minimizes unexpected breakdowns. It also extends the lifespan of the entire hydraulic system.
Guidelines for Counterbalance Valve Component Replacement
Replace worn or damaged components promptly. Use only genuine manufacturer parts. This ensures compatibility and performance. Technicians should follow detailed service manuals for disassembly and reassembly. Calibrate the valve after any major component replacement. Proper replacement prevents cascading failures. It maintains system integrity and safety.
Informed counterbalance valve selection is paramount for hydraulic systems. It directly leads to optimal efficiency, enhanced operational stability, and superior safety. Professionals must continuously learn about these critical hydraulic system components. This ongoing knowledge ensures peak performance and reliability.
FAQ
What is the primary function of a counterbalance valve?
A counterbalance valve primarily prevents uncontrolled load movement. It holds a load in position and controls its descent speed. This ensures system safety and stability.
How does the pilot ratio affect valve performance?
The pilot ratio influences valve sensitivity. A low ratio enhances stability, while a high ratio provides smoother operation. Engineers align the ratio with application needs.
What are common signs of a malfunctioning counterbalance valve?
Common signs include load drift, chatter, or instability. External leakage and overheating also indicate potential issues. Prompt diagnosis prevents further system damage. ⚠️





